Total station search
Fluorine lined butterfly valve pneumatic butterfly valve electric butterfly valve
Worm drive 1: gearbox

Serial connection of three worm drives. The input end is a yellow worm gear, and the output end is a pink worm gear, which are coaxial. The transmission ratio of each driver: i1, i2, i3. Total ratio i=i1 × I2 × I3=30 × twenty × 20=12000.
Worm drive 2: gearbox
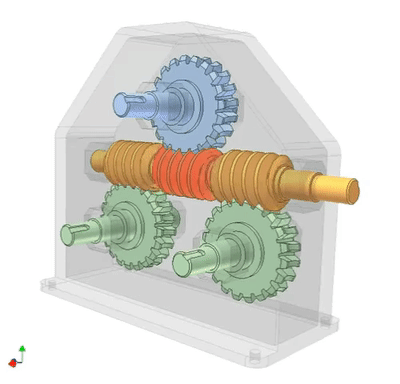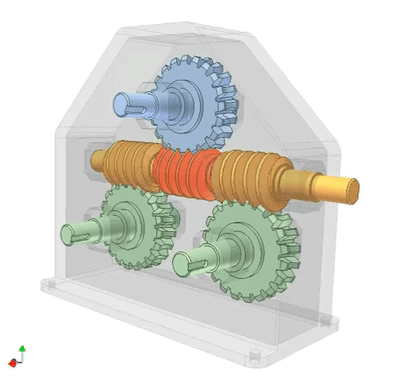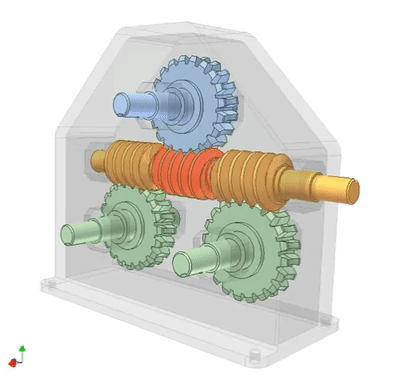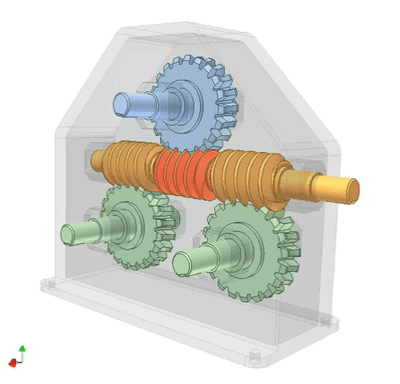
A screw drives three gears simultaneously, and the gear shaft is at right angles to the axis of the screw. This structure can replace more expensive gear units.
Worm Drive 3: Rolling Worm Gear
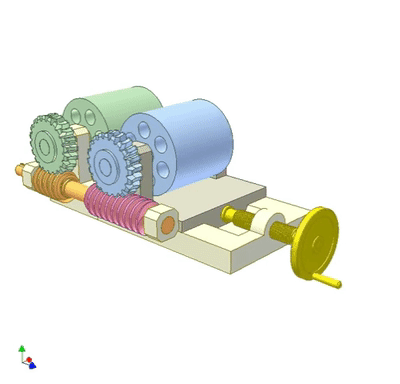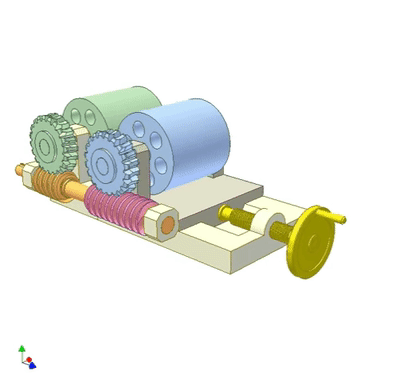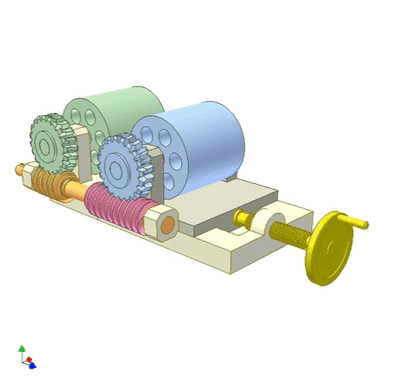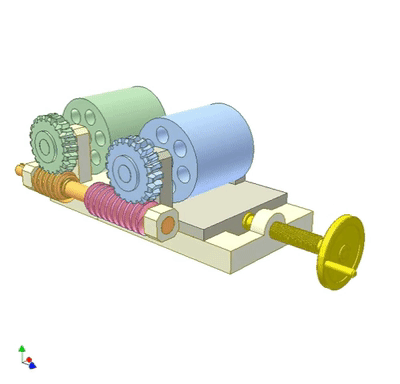
The worm gear rolls on the worm to adjust the wheelbase of the two rollers.
Worm Drive 4: Rotating Rolling Worm

The machine tool turntable rotates the worm around its axis and simultaneously rolls on the worm gear.
Worm transmission 5a: rotating and parallel moving worm

In addition to rotation, the input worm also moves longitudinally through a cylindrical cam, and the worm gear rotates in the opposite direction.
Worm transmission 5b: rotating and flat shifting worm

Worm drive is compensated by a cam on the working shaft, generating intermittent movement of gears. The input end is on the green axis. There is a positioning joint between the orange single head worm and the green shaft.The pink cam is stationary. The cam profile is composed of two spiral curves with opposite directions, and the pitch of the curve is equal to the pitch of the worm. The red spring maintains contact between the cam and the purple pin.Rotate the input one revolution, keep the gear stationary, and then rotate one tooth.
Worm drive 6: gears rotating around the worm

The gear rotates around the worm, and the red mark indicates that the gear rotates around its axis. Complete one rotation around the worm gear shaft, and the gear rotates Z1/Z2 around the shaft. Z1: Number of threads for the worm. Z2: Number of teeth of the gear.
Worm Drive 7: Rotating and Rolling Worm Trajectories

The worm rotates around its axis while rolling on the gear. The points of the worm (in a plane perpendicular to the worm axis and containing the wheel axis) move along the circular helix (green). Points that are not in the plane are tracked by a diagonal circular spiral (orange).
Worm Drive 8: Gears that rotate around the trajectory of the worm

The gear rotates around the shaft and worm simultaneously. The orange line is the trajectory of the gear points, located in a plane perpendicular to the gear axis and containing the worm shaft. The distance from this point to the gear shaft is equal to the shaft distance between the worm and the gear.
Worm drive 9: roller

The wheels are equipped with rollers to reduce friction losses.
Worm Drive 10: Spring Worm
Springs provide another way of transmission for worms, helping to absorb strong vibrations.
Worm drive 11: spring worm, pin wheel

Springs and pins provide an alternative to worm and worm gear transmission.
Worm Drive 12: Multiplying Gear

The input end is a green wheel, and the orange output worm has a large pitch thread.
Worm drive 13: slotted wheel

The grooves on the thin wheel rims provide another way of producing wheels.
Worm drive 14

The two movements of the orange worm: rotation and horizontal movement cause the green gear to rotate in the opposite direction. Note: If three spur gears are arranged on the same line (the orange intermediate gear meshes with the blue and green gears), the blue and green gears rotate in the same direction. Even during transmission, the relative angular position between gears can be adjusted.
Worm - Worm Drive 1
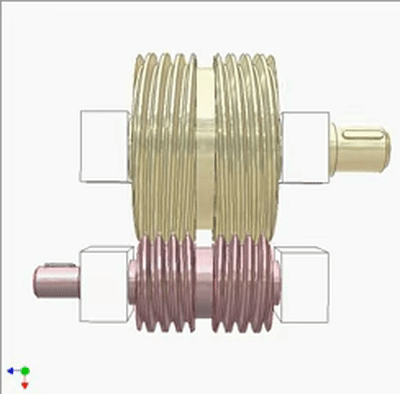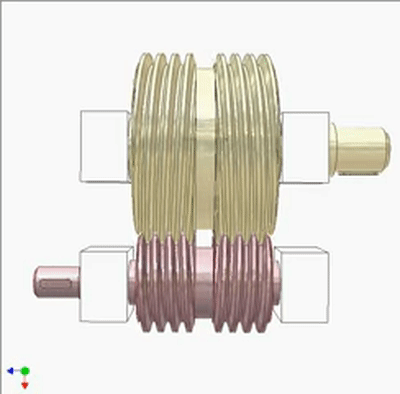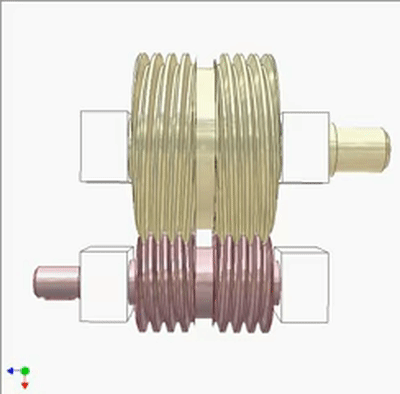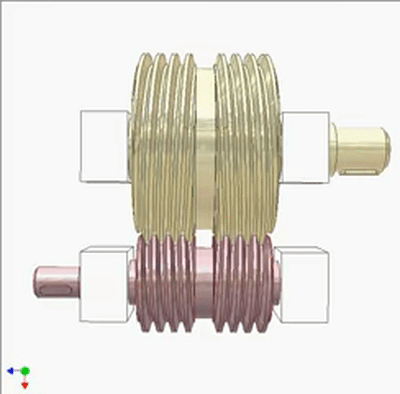
Worm - Worm Drive 2
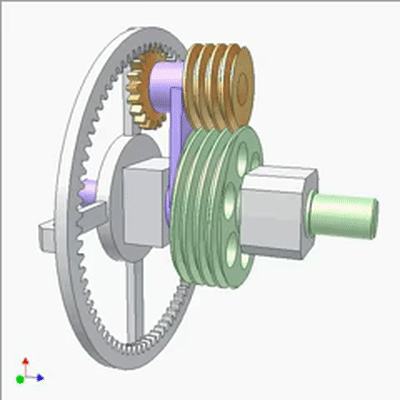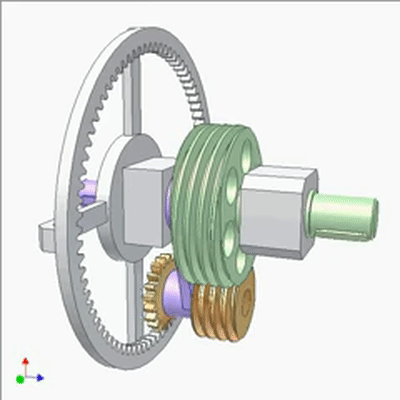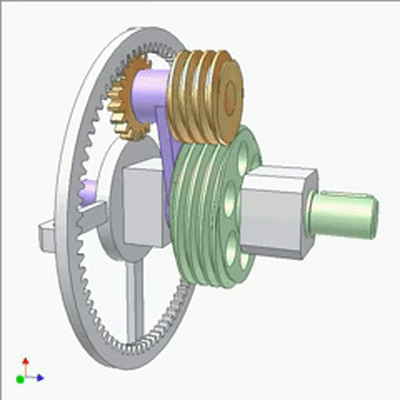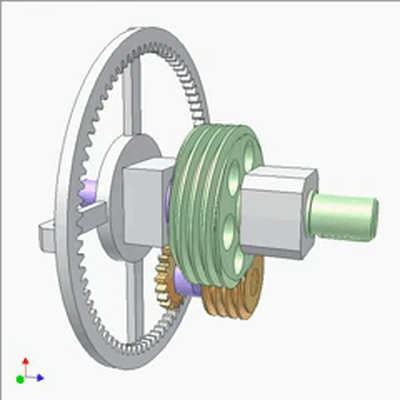
Research on Worm Drive 1
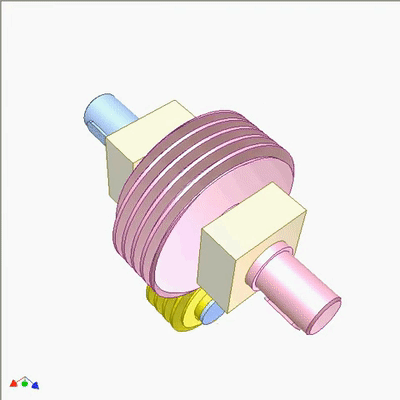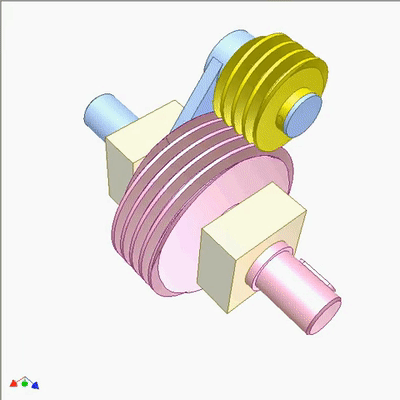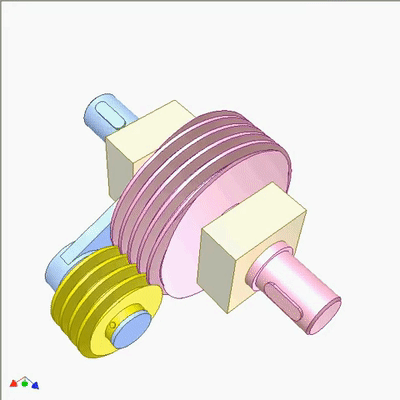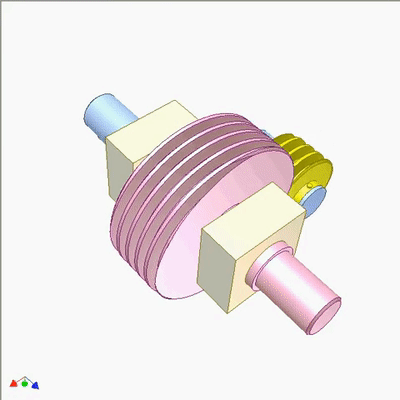
The input end is fixed with a yellow small worm (1 head, lead t1, pitch diameter D1) on the blue crank. The output end is a large worm (2 heads, lead t2=2t1, pitch diameter D2=2D1). The output and input rotate at the same speed and direction. Small worms can be replaced by cylindrical circular grooves or racks. If the yellow worm has a rotating joint with the crank and there is sufficient friction between the worms, the output and input also rotate at the same speed and direction (the yellow worm does not rotate on its pivot).If not, the output rotates slower than the input. The diameter of the worm does not play a significant role in kinematics.
Research on Worm Drive 2

Research on Worm Drive 3
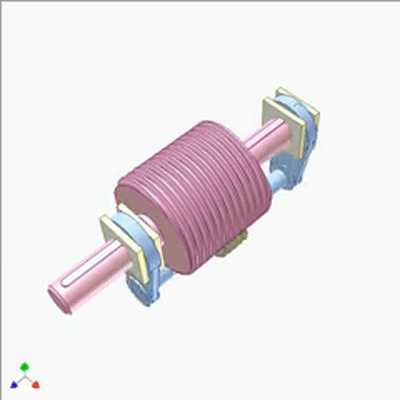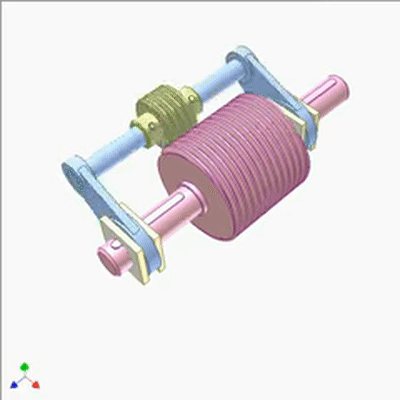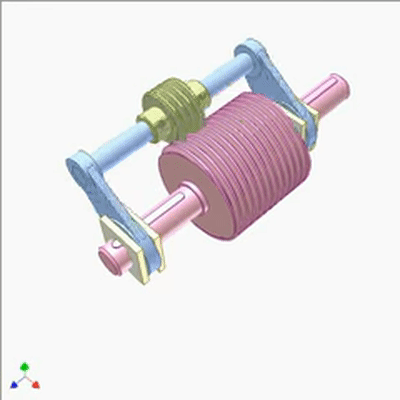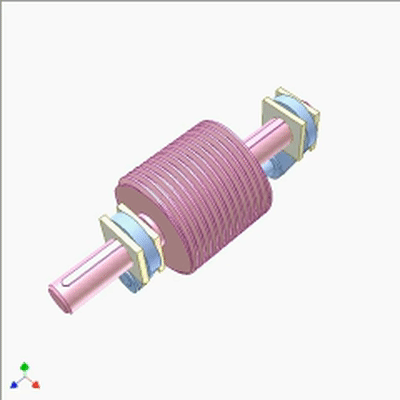
行星蜗杆传动研究1
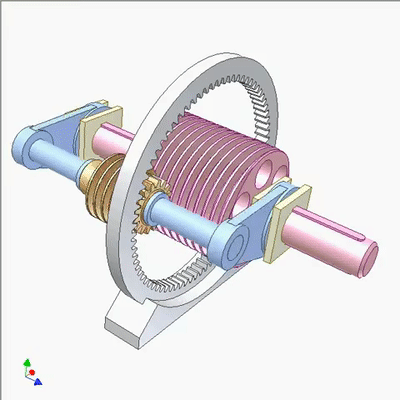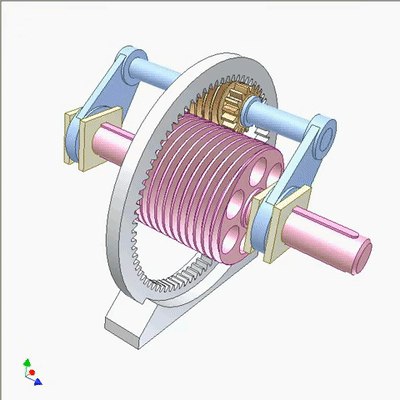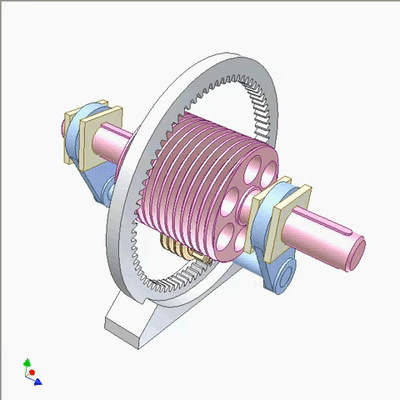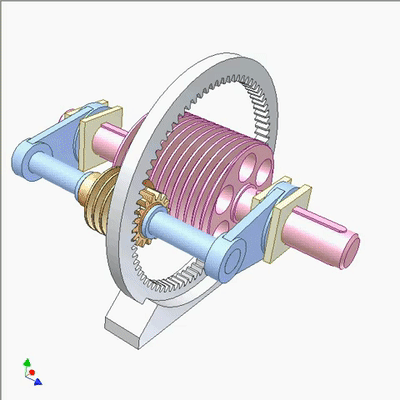
Research on planetary worm drive 2

Double worm drive 1
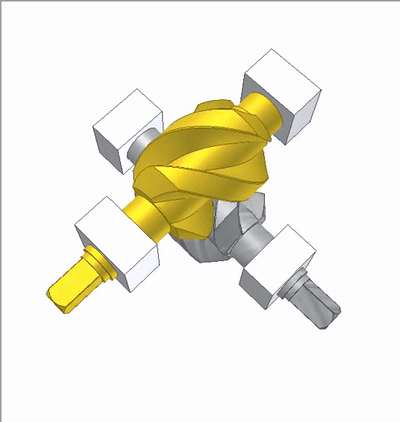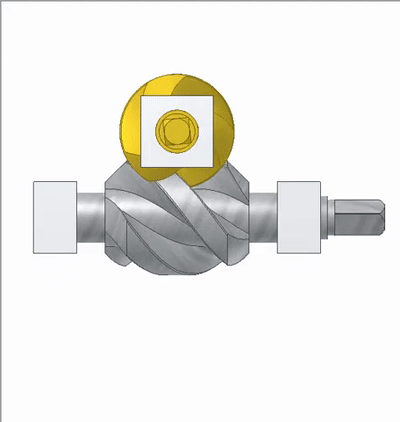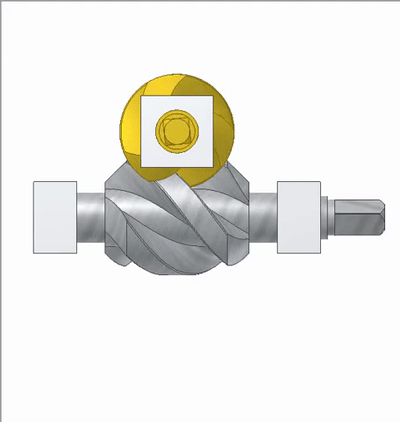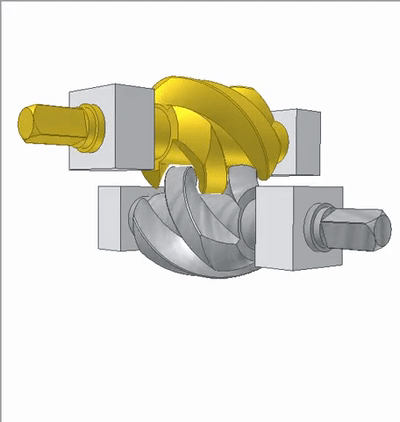
The lead angle of the worm thread is 45 degrees. The transmission ratio is 1:1, which is a 90 degree variable direction transmission.
Double worm drive 2

The white worm is stationary. The yellow bracket rotates around the white worm shaft (speed S1), which causes the blue worm to rotate around its own axis (speed S2), S1=S2. The threads of two worms are the same, and the lead angle of the worm thread is 45 degrees.
Double worm drive 3

The two worms are the same and inclined at 90 degrees. The lead angle of the worm thread is 45 degrees. The white slider is stationary.
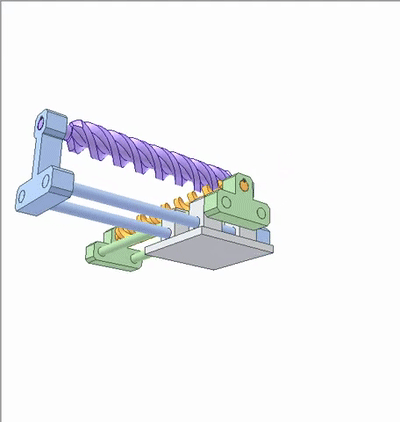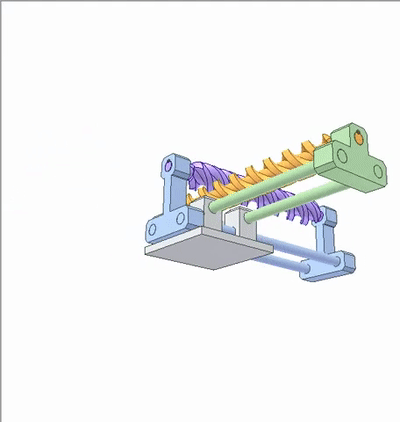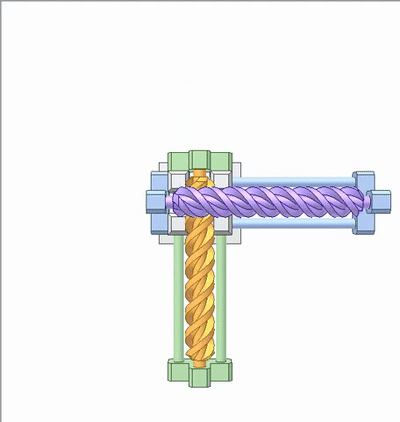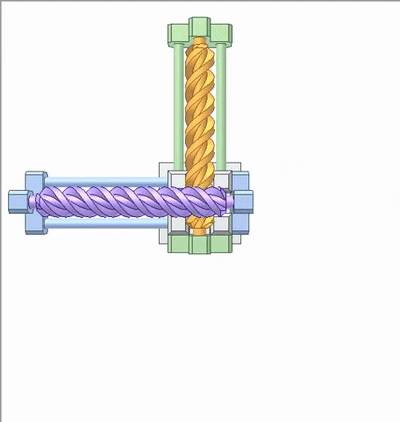
The movement of the green slider carrying the orange worm causes the blue slider to carry the violet worm. The transmission ratio is 1, which can be called a spiral wedge mechanism.
Double worm drive 4

The two worms are inclined at 90 ° and the threads are the same. The lead angle of the worm thread is 45 °. The pink worm is stationary. When the green worm rotates, the blue slider moves along the spiral raceway.

When the rack is not needed, this mechanism can replace the gear rack mechanism. The disadvantage is low efficiency. Reduce the lead angle of the pink worm to improve efficiency. In that case, the green worm becomes a helical gear.
Worm gear transmission

The axis of the orange gear and blue worm is inclined by 90 °. The fixed worm has 1 head and the number of gear teeth is 3. When the orange gear rotates, the green slider moves along the spiral raceway.

Keep the direction unchanged during rotation


Tel: 022-86927931
Mobile phone: 18502628839
Email: Mr.ye@crdvalve.com
Address: NO.1 Rongsheng Road, Xiaozhan Industrial Zone, Jinnan District, Tianjin